Nutrition
I always tell my students that we get only one body in this lifetime and the foods we put into it determine what we get out of it.
We can spend days exploring diets, fads, and the quick fixes when it comes to weight and health, however I am a strong believer in making a clean nutrition a lifestyle and not just an event.
There are no quick fixes or easy solutions when it comes to nutrition, but instead healthy and consistent habits we create, hard work and dedication towards eating clean, and most importantly understanding there is no "one size fits all" approach one it comes to diet.
We all have unique bodies, have different wants and needs when it comes to food, and perceptions and experiences about eating.
Ultimately, it is up to you to explore food in fun and meaningful ways and to find a plan that is realistic, achievable, and that makes you feel and look your best!
We can spend days exploring diets, fads, and the quick fixes when it comes to weight and health, however I am a strong believer in making a clean nutrition a lifestyle and not just an event.
There are no quick fixes or easy solutions when it comes to nutrition, but instead healthy and consistent habits we create, hard work and dedication towards eating clean, and most importantly understanding there is no "one size fits all" approach one it comes to diet.
We all have unique bodies, have different wants and needs when it comes to food, and perceptions and experiences about eating.
Ultimately, it is up to you to explore food in fun and meaningful ways and to find a plan that is realistic, achievable, and that makes you feel and look your best!
Where it all should begin!
Vitamins, Minerals, and Fats, oh My!
Vitamins
There are 13 essential vitamins that are critical to living! Essential vitamins are 1 of 4 groups of essential nutrients that a human being needs.
The other 3 being (minerals, essential fatty acids, and essential amino acids.) Vitamins play a critical role in normal cell function, growth, and also in development.
There are 2 essential groups of 13 total vitamins:
4 Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) and they are stored in the body's fatty tissue. These 4 are easily absorbed with dietary fat.
9 Water-soluble vitamins (B6, B12, C, Biotin, Niacin/B3, Folate, Pantothenic Acid/B5, Riboflavin/B2-can be stored for years in liver, Thiamine/B1 are used immediately with the leftovers getting flushed out through the urine.
Where to get them and what they do:
The other 3 being (minerals, essential fatty acids, and essential amino acids.) Vitamins play a critical role in normal cell function, growth, and also in development.
There are 2 essential groups of 13 total vitamins:
4 Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) and they are stored in the body's fatty tissue. These 4 are easily absorbed with dietary fat.
9 Water-soluble vitamins (B6, B12, C, Biotin, Niacin/B3, Folate, Pantothenic Acid/B5, Riboflavin/B2-can be stored for years in liver, Thiamine/B1 are used immediately with the leftovers getting flushed out through the urine.
Where to get them and what they do:
Vitamin |
What it does |
How to get it |
Vitamin A |
Form and maintain bones, soft tissue, mucous membranes, healthy skin and teeth |
Dark colored fruits and veggies, egg yolks, liver, fish, beef, some cheeses, yogurts, butters, and creams |
Vitamin C |
Antioxidant that promotes healing, helps body maintain healthy tissue and absorb iron |
Broccoli, cauliflower, brussel sprouts, spinach, citrus fruits |
Vitamin D |
Helps body absorb calcium to help maintain healthy bones and teeth |
Fatty fish, dairy products, and humans produce from sunlight |
Vitamin E |
Antioxidant (tocopherol) that helps body make red blood cells and utilize Vitamin K |
Nuts, seeds, avocado, dark-green veggies, oils (sunflower, corn, safflower) |
Vitamin K |
Bone health, and coagulation of blood |
Dark-green veggies and leafy greens, eggs, beef, fish |
Niacin (B3) |
Maintain healthy skin and nerves/ function |
Eggs, avocado, fish, legumes, nuts, poultry, fortified breads |
Vitamin B6 |
Brain function, and helps form red blood cells |
Bananas, legumes, poultry, meats, nuts, avocado, whole grains |
Vitamin B12 |
Metabolism, maintain central nervous system, form red blood cells |
Eggs, shellfish, poultry, milk |
Pantothenic Acid (B5) |
Production of hormones, cholesterol, and metabolism of food |
Dark-green veggies, eggs, lentils, legumes, poultry, sweet potatoes, whole-grain cereal, milk |
Thiamine (B1) |
Changes carbohydrates into energy |
Eggs, lean meats, nuts, legumes, whole grains |
Folate |
Works with B12 to create red blood cells and production of DNA for tissue growth and overall cell function |
Leafy greens, peanut butter, beets, beans, lentils, green veggies |
Minerals
Minerals are another essential vitamin that your body needs, however they can't produce them. The body uses these inorganic substances found within particular foods.
There are 2 types that contribute towards bone and teeth, energy, immune health, and nerve/muscle function.
Macro-minerals (Calcium, Potassium, Sodium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Chloride, and Sulfer)
Trace Minerals (Iron, Zinc, Selenium, Manganese, Copper, Iodine, Cobalt, and Fluoride)
There are 2 types that contribute towards bone and teeth, energy, immune health, and nerve/muscle function.
Macro-minerals (Calcium, Potassium, Sodium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Chloride, and Sulfer)
Trace Minerals (Iron, Zinc, Selenium, Manganese, Copper, Iodine, Cobalt, and Fluoride)
Mineral |
What it does |
How to get it |
Calcium |
Bone development, heart beat regulation, and blood clotting |
Dairy products, nuts, eggs, shellfish |
Potassium |
Energy and electricity transferred properly between cells to ensure nerve impulses and heart rhythm |
Fruits, potatoes, fish |
Sodium/Chloride |
Absorbs and transfers nutrients, maintains blood pressure and right balance of fluid, contracts/relaxes muscles |
Vegetables, seaweed, rye, tomatoes, celery, olives |
Phosphorus |
Bone and teeth health, metabolizing energy into strength |
High protein foods, poultry, meats |
Magnesium |
Healthy thyroid, and bone health |
Green leafy vegetables, nuts, soybeans, cocoa |
Sulfur |
Muscles, skin, and bone health, and is used to create protein for cells, tissues, hormones, enzymes, and antibodies |
Cruciferous veggies, garlic, onions, broccoli, eggs, dairy |
Iron |
Part of hemoglobin that helps with blood production and oxygen delivery |
Red meat, spinach, shellfish, legumes, quiona |
Zinc |
Immune health, taste, and smell senses |
Eggs, legumes, nuts, whole-grains, meat, dairy |
Selenium |
Thyroid function, DNA production, protection from free radicals |
Lean meats, nuts, eggs, legumes |
Manganese |
Normal brain and nerve function, formation of connective tissue |
Leafy green vegetables, legumes, seeds, tea, whole-grains |
Copper |
Forms red blood cells, healthy blood vessels, nerves, and bones while helping absorb iron |
Whole-grains, leafy greens, nuts, potatoes, cocoa |
Iodine |
Makes thyroid hormones and controls metabolism |
Sea vegetables, eggs, yogurt, prunes |
Cobalt |
Making red blood cells, maintaining nervous system and nerve cells |
Whole-wheat/Whole-grains, cocoa, chocolate, legumes, teas |
Fluoride |
Protects teeth from decay and cavities |
Water, teas, raisins, fruits and veggies, |
Amino Acids
Amino Acids are found in two kinds:
Essential (your body can't produce)
Non-Essential (your body/liver can produce)
Both are organic compounds needed for biological processes and are critical pieces to all the tissues in the human body.
Essential (your body can't produce)
Non-Essential (your body/liver can produce)
Both are organic compounds needed for biological processes and are critical pieces to all the tissues in the human body.
Essential Amino Acids
Essential Amino Acid |
What it does |
How to get it |
Lysine |
Building a healthy immune system |
Fish, eggs, cheese, potatoes |
Isoleucine |
Muscle development and repair |
Eggs, meats, lentils, soy protein |
Leucine |
Nitrogen balance and energy supply |
Soybeans, beef, peanuts, pork, fish, almonds, chicken, lentils, oats, chickpeas, corn, rice, dairy |
Methionine |
Process and remove fat |
Lentils, garlic, meats, fish, onions, yogurt, eggs |
Phenylanine |
Forms important brain chemicals (neurotransmitters and hormones) |
Poultry, beef, fish, nuts, cheese |
Threonine |
Cardiovascular system, central nervous system, immune and liver function |
Leafy vegetables, meats, nuts, grains |
Tryptophan |
Produces serotonin which fights depression, weight gain and other health problems |
Turkey, beef, fish, brown rice, soy protein |
Valine |
Energy provision and regulates blood sugar |
Meats, mushrooms, nuts |
Histidine (semi-essential) |
Essential for infants in growth and development |
Fruits and veggies |
Non Essential Amino Acids
Non Essential Amino Acids |
What it does |
Where to find it |
Alanine |
Removes toxic substances produced from exercise |
|
Asparagine |
Helps nervous system maintain equilibrum |
|
Aspartate |
Combats fatigue and depression |
Value |
Cysteine |
Component of protein for healthy nails, skin, and hair |
|
Glutamate |
Promotes healthy brain function |
|
Glycine |
Skin and wound healing |
|
Proline |
Creates healthy new cells |
|
Serine |
Synthesis of immune system proteins |
|
Tyrosine |
Brain function and synthesize neurotransmitters |
Meats, dairy, fruits, seeds |
Arginine |
Biosynthesis of proteins |
Turkey, pumpkin seeds, soybeans, chicken |
Glutamine |
Muscle recovery, healing wounds, kills infections |
Essential Fatty Acids
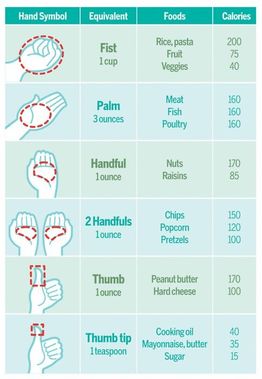
How to Eat
What to Eat
|
|
|
Feed your Brain
|
|
|
|
|
|